The Art of the Pitch: Understanding Roof Slopes and Angles
In this article, we will explore the art of the pitch, discussing the various roof slopes and angles commonly used in construction.
Importance of Roof Slopes
The slope of a roof refers to the steepness or angle at which the roofline inclines. Roof slopes are a critical design element as they impact the overall look of a building, its structural integrity, and its ability to shed water. In regions with heavy rainfall or snowfall, a steeper roof slope is typically recommended to prevent water buildup and ensure proper drainage. Conversely, in drier climates, a shallower roof slope may be sufficient.
Common Roof Slopes
Roof slopes are typically expressed as a ratio of rise to run, such as 4:12 or 6:12. This ratio indicates the vertical rise in inches for every 12 inches of horizontal run. A 4:12 slope, for example, would rise 4 inches for every 12 inches of horizontal distance. Common roof slopes range from 2:12 (low slope) to 12:12 (steep slope), with a 4:12 slope being considered a standard pitch for most residential roofs.
Types of Roof Angles
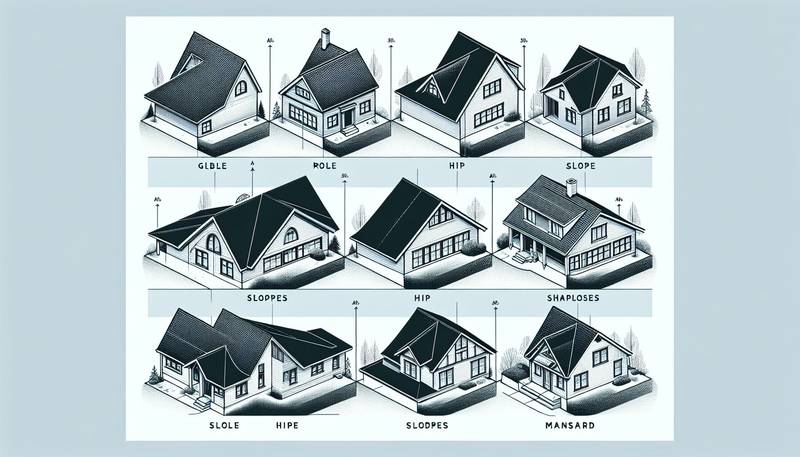
In addition to slope, roof angles play a significant role in the overall design and functionality of a roof. The most common roof angles are the gable, hip, and shed. A gable roof features two sloping sides that meet at a central ridge, forming a triangular shape. Hip roofs have four sloping sides that meet at a ridge, with all sides sloping downward from the center. Shed roofs have a single slope and are commonly used for additions or modern architectural designs.
Calculating Roof Pitch
Roof pitch is determined by the rise and run of a roof, which can be calculated using various methods. One common method is to measure the vertical rise from the top of the roof to the bottom (the rise) and the horizontal distance from the center of the roof to the edge (the run). By dividing the rise by the run and multiplying by 12, you can determine the roof pitch in inches per foot. For example, a roof with a 6-inch rise and a 12-inch run would have a pitch of 6:12.
Design Considerations
When designing a roof, it is essential to consider the desired slope and angle to meet the functional and aesthetic requirements of the building. Factors such as climate, architectural style, and building codes will influence the optimal roof pitch and angle for a specific project. Consulting with a professional architect or engineer can help ensure that the roof design meets all necessary criteria for safety and performance.
Conclusion
The art of the pitch involves understanding the various roof slopes and angles and how they impact the overall design and functionality of a building's roof. By choosing the right pitch and angle for a roof, architects and builders can create a structure that is both visually appealing and structurally sound. Whether it be a gable, hip, or shed roof, careful consideration of the slope and angle is essential for a successful roofing project.